Approved: Fortect
If you get a Lisrel error on your computer, this guide can help you.
1. Access to LISREL in terminal server systems
2. An example of Heywood and LISREL
3. An indefinite matrix of positive and different covariances. General coefficient for determining physical equations
5. P-value coefficient for tests
6. Reading missing data directly into LISREL
7. Comparison of LISREL groups
with 8. Score l ‘fashionable identification
9 LISREL Access Violation in Kind of Terminal Server Statistics Applications
Access To LISREL In Terminal Server Systems
Question:
Where is Lisrel’s structural equation modeling system available for timeshare systems?
Answer:
LISREL is only available for Stat-Apps-Server. Lisrel 8 is a standalone product that can read a wide variety of data sets. Visit the Stat Apps Server page to learn how to connect to the Stat Apps Server.
Episodes Of Haywood And LISREL
Question:
I am using LISREL 8 which helps some to model structural equations and have problems with repetitive errors. This message says: WARNING: EPS Theta is NOT DEFINED TO BE POSITIVE. As a result, youAnd indices, change t-values, remainders, etc. cannot be computed, and I assume that the estimates of the continuation parameters are a bit arbitrary. Is there a solution for this?
Answer:
The Covariance Matrix Cannot Be Measured Unambiguously
Question:
When I run my data, I get an error that the group covariance matrix is not positive definite. I have searched in the LISREL book I have and it does not provide an explanation for this error message. Ratio
Answer:
Sum Of Solution For Structural Equations
Question:
I am using LISREL. I used my attached prints in LISREL 7 to get a statistic called “general coefficient with definition for structural equations.” I cannot get them with i LISREL 8. How can I get this knowledge with LISREL 8?
Answer:

The LISREL authors decided not to include statistics in the available edition of LISREL. This means you need to compute it in order to run in other parts of the LISREL output.
P-values for Odds Tests
Question:
I often use LISREL to create structural equation models. LISREL models coefficient estimates, standard errors, and then t-values for each path, but I don’t need to see the p-value associated with its t-values. How do I know if my route is important?
Answer:
The authors of the LISREL software assume, for better or worse, that LISREL users will use sample sizes well above 120, the point at which most platforms in the t distribution of t have infinite assignment value. At this element, the t-distribution can essentially be approximated to the z (standard normal) distribution.
For a distribution, a value of less than -1.96 and even greater than +1.96 indicates a statistically really serious result with an alpha value of 0.05, two-sided. The critical value is step 1 – / + 64 for a one-sided test.
For an alpha of 0.01, the critical Z-values are usually – / + 2.58 a for a two-sided test, – / + 2.33 for a one-sided test.
A proven null theory is that the coefficientPt is simply statistically significantly different from zero, while the null hypothesis can be tested against the correlation value or zero weight of the regression test in the population d ‘of the person from whom your sample was taken.
In practice, you do not need to evaluate the t values obtained from the LISREL expression on your a unless your sample size in table t is 120 or less cases. Alternatively, if the sample is large enough (or if you are willing to make this assumption with this smaller sample), you can evaluate your advantage of t as shown in the LISREL expression over the critical value of z. You choose based on your choices in terms of alpha level. If your value is likely to be greater than the positive cutoff, possibly less than the negative cutoff, then reject the null hypothesis and assume that the path factor is significantly different from zero. Instance,
Let’s say you chose the amazing alpha level of 0.05, two-sided. Therefore, the critical values of t will remain -1.96 and +1.96. If you receive aBy taking 2.92, you will reject the null hypothesis. Likewise, if you got a value of -2.45, you would also object to the hypothesis of zero. On the other hand, if you get a t value of 1.76, you will not reject the null hypothesis. In the latter case, there will probably not be enough evidence that the path factor was often significantly different due to zero in the population from which you should be selected.
Read Missing Data Directly Into LISREL
Question:
Approved: Fortect
Fortect is the world's most popular and effective PC repair tool. It is trusted by millions of people to keep their systems running fast, smooth, and error-free. With its simple user interface and powerful scanning engine, Fortect quickly finds and fixes a broad range of Windows problems - from system instability and security issues to memory management and performance bottlenecks.

I am using LISREL to read raw personal data directly instead of preprocessing an article with PRELIS. I know I can use the MISSING = 99 option in PRELIS. You can tell PRELIS that 99 are the missing points on disk in my data file. Is there something similar for you that I can use LISREL?
Answer:
Yes, now with me. Can you use the XM = 99 option on the LISREL DA command line? If your underlying missing value code is other than 99, replace the ninety-nine value in the above statement with a missing data code.
Show Poksay
For Questions 7, 8 And 9 – Click On The Links Below:
9. LISREL Access Violation via Terminal Server Statistics Applications
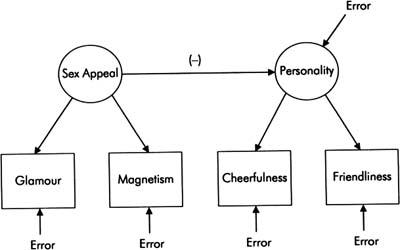
LISREL’s Theta-Epsilon-EPS) (Theta-Matrix is an entanglement matrix associated with Y residuals (ie, customizable residuals downstream). An estimate of the negative variance in its matrix makes it “undefined positive”; variance because the measurement error is terrible. Negative variance estimates are the result of similarity (the quadratic correlation between the latent variable and the measurement variable) greater than 1.00.
This situation is referred to as the Haywood case in the factor analysis literature. Heywood’s cases have many possible causes, including data loss, previous poor grades, and a poorly defined model. Therefore, possible solutions include collecting more data, more accurate preliminary estimates, and simply identifying a more suitable model.
Possible solutions for the successful concatenation of computer code include: a) providing better historical estimates, and b) usingdifferent methods of evaluating resolution.
A) Replace initial values with defacto: some users have had moderate success with ST .5 ALL.
B) Replace the standard maximum likelihood solution with the usual least squares or generalized least squares solution, as the first method is now especially vulnerable and gives Heywood cases. Conventional least squares methods, i.e. generalized least squares solutions, are available by testing UL or GLS on OR cable.
The wrong model can also produce Heywood boxes; one example is called “empirical sub-identification”. This happens when there are countless solutions to design values (parameter estimates). This is especially safe when the correlation or covariance matrix that associates hidden variables with computed variables has only a small number of results (for example, only one or two measured variables for each individual hidden variable). whether the prevailing error in estimates is large. You can easily try to get around this laboruse the EQ instructions to set the remainder to 1.
Heywood boxes are a software problem. SAS added all of the HEYWOOD parameters to the CALIS process, leaving common scores 1.0 to 7 higher.
This notification usually means that one or more of the following events are occurring:
1) There is usually redundancy between correlation matrices – in other words, correlations can be a linear function of some of the different correlations.
This problem can be solved by deleting these redundant variables or collecting additional data.
2) Maybe model more parameters for you, so you need degrees of freedom. You can test this by checking how many degrees of freedom you have as the number of parameters you are already guessing. Formula
which is used to calculate the number of values of freedom ava
Speed up your computer's performance now with this simple download.