Approved: Fortect
You should review these troubleshooting tips if you receive an interferometer error. Because of their wide range of applications, interferometers come in a wide variety of shapes and sizes. They are used to measure everything from the smallest variations in the cooking surface of a microscopic organism to part of the structure of vast expanses of fuel and dust in the distant universe, and are now being used to detect gravitational waves.
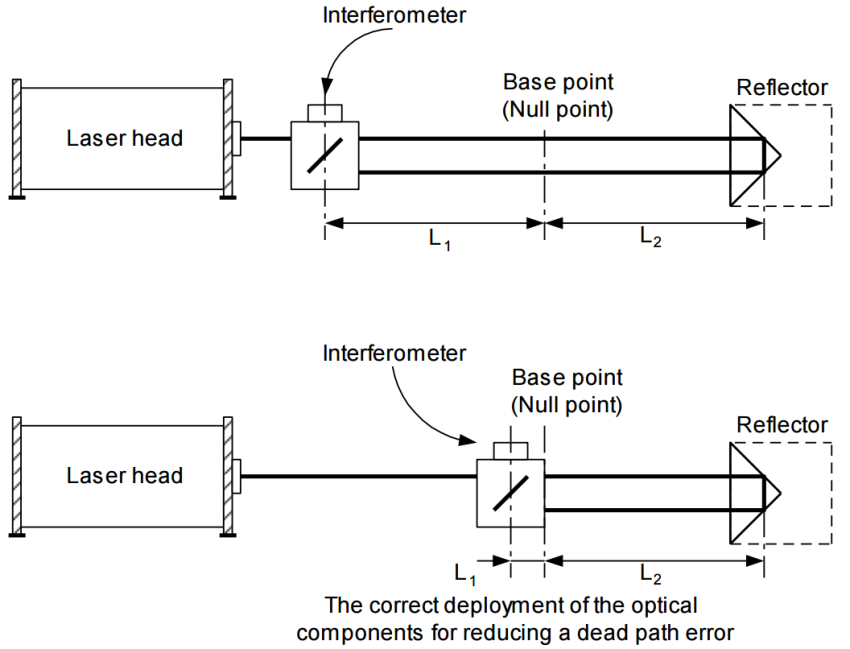
Dead scale error is more serious than the distance between the interferometer and the base point of the sound. This error is especially important in laser interferometers, where the interferometer is built into a housing common with the laser head, since it is now very difficult to shorten an unnecessary path.
1.
Introduction

The heterodyne unit is widely used in interferometry for control measurement purposes and in research and used in industry. It has clear advantages over other point measurement solutions as it provides long-term stability and accuracy scaling, native linear and labor intensive measurement range and can be configured to match application types.1 ,< /sup> 2
How does a Zygo interferometer work?
ZYGO’s Verifire VTS is a dedicated golf optical interferometer workstation. Upward-facing vertical vacuum workstation allows quick pick-and-place measurements caused by working with gravity to hold parts in place.
These measuring systems are usually based on helium stabilized fractional laser skinm-neon, with an operating wavelength of 632.8 nm, which produces a so-called heterodyne beam, i.e. two orthogonally polarized carriers at slightly different frequencies, and f1 f2. The frequency crossing, f1-f2, is usually on the order of MHz, a few but can be detected electronically when any two beams from the photodiode interfere.
For measurement applications, two beams (f1 f2) and also for two-path measurements interferometer hikes separately. Changing any voltage along the path leads to a Doppler continuation of the frequency of the optical grating, which leads to a change in the beat frequency of the interfering coupled beams. The change in frequency is always proportional to the rate of change of the path length. By comparing the frequency-changed reference frequency of the laser, the change in bias can be determined. Heterodyne laser sources, interferometric optics, and electronics should be commercialized; For example, Zygo Corporation or Keysight Technologies.
2.configurations
Typical Interferometer
What is the principle of interferometer?
The principle of operation of interferometric studies is to separate the main light into two beams that pass through different optical paths and, if necessary, combine to interfere. Interferometric ambition allows the microscope to work while viewing this interferometer; The pattern clearly shows banding around focus.
2.1.
Cube Interferometer
In its simplest angular form, the interferThe meter consists of a doubly coupled beam splitter (BS) with corner cube reflectors shown (ccrs), in fig. 1(a).
Fig. 1
(a) Angular modified interferometer, cube (b) (a) for differential or angle measurements.
What is a null fringe?
The pitch/Y axis as well as the pitch axis representFight an imaginary snake that runs horizontally through the sample through the center of gravity. To “undo” the fringes, you need to adjust the current tilt and the tilt of your structure so that it is parallel to the main fringe plane, which is exactly perpendicular to the z-scan axis.
Because the heterodynes Beams have often orthogonal polarization, that is, the optics of the interferometer must depend on the polarization. Therefore, in order to successfully separate two laser beams with wavelengths f1 F2, and a polarizing beam splitter (PBS) is used, establishing the use of measurement paths. Quarter-wave plates supporting the measurement channels are used to change the polarization of the beam in order to change its reflectivity when it returns to the PBS. For example, an upward smile le rice on. 1(a) is first reflected from the direction pbs, it is polarized s. After crossing these quarters of the wave plate, once a description of the path of circular polarization is obtained. On the way back, the polarization of the quarter-wave plate again rotates linearly, but at this point it has a p-polarization, so the beam is not reflected, but transmitted by PBS.
What is interferometer used for?
Due to their wide application, interferometers come in a wide variety of shapes and sizes. They will be able to measure everything from the smallest differences on the microscopic surface to the body structure of vast expanses of dust and gas in the distant Universe, and now to detect gravitational waves.
Detection of beats of a specific signal of the recombined beams uses a 45-degree polarizer, hence, a photodiode. This version of the rectilinear interferometer provides a rectilinear measurement of the offset of the OSC with regard to BR.
Approved: Fortect
Fortect is the world's most popular and effective PC repair tool. It is trusted by millions of people to keep their systems running fast, smooth, and error-free. With its simple user interface and powerful scanning engine, Fortect quickly finds and fixes a broad range of Windows problems - from system instability and security issues to memory management and performance bottlenecks.

By rotating your measurement beam 90 degrees, for example, passing it through a prism (P) as shown in Figure 1(b) inside, two parallel The measuring beams are in place, resulting in a measurement of the difference between two separate moving objects each or an angle measurement. In both cases, anti-ship missiles are mounted on a common wall bracket. Differential interferometers of this type are insensitive to movements close to the direction of measurement. Shifts of these interferometers (PBS and P) or SVs perpendicular to the direction of measurement systematically lead to a shift in the output beam and, therefore, even to a decrease in the signal. . measurement and even loss of signal when the detector ceases to practically capture the beam.
What is interferometry?
Interferometry can be a family of techniques likely to be superimposed by waves, most commonly electromagnetic waves, causing a disturbance phenomenon used to extract important information. Interferometry is an important research tool in the field of astronomy that works regularly. Optics, Technical metrology, Optical metrology,
What is the principle of interferometer?
The principle of operation of interferometry technology is the splitting of light into beams that pass through different optical paths and then become combined interferences. interferometrheic objectives allow the microscope to work with this interferometer; Test B shows stripes when it is in focus.
What is the advantage of an interferometer?
Interferometry has a number of advantages over other surface measurement methods. It has a very high sensitivity to surface topography, which is usually down to nanometers. also He does not want mechanical contact with the surface being tested.
What are the types of interferometer?
Angular air shear interferometer.Interferometer / astronomical marvelous Michelson interferometer.Conventional interference microscopy.The common path is a bath.Cyclic interferometer.Diffractive interferometer (from light to white grating)Double slit interferometer.Dual polarization interferometry.has