Over the past few weeks, some users reported that they often encounter error messages with XP.
Approved: Fortect
Microsoft Windows XP systems are typically fatal for a variety of reasons and for several reasons. Some of these glitches are minor and can be easily fixed by simply closing the unresponsive application or restarting the system. Others, however, are more serious and can bring the entire system to its knees. Microsoft calls this type of failure a “stop failure” because the system stops responding. When a Stop error occurs, the GUI will almost certainly be replaced by a DOS-like blue screen in a cryptic error message followed by a code number. This screen is affectionately referred to as the ‘blue screendeath “or BSOD for short.
I’ll show you how to parse BSOD snippets and hence related troubleshooting information. Next, I’ll take a look at some of the fairly common BSOD errors in Windows XP. I will also provide a link to a Microsoft Knowledge Base article that details the troubleshooting steps and possible solutions. To see screenshots of these BSOD error messages, along with an explanation of each one, check out this photo gallery.
This article is also available in PDF format as part of the TechRepublic download.
BSOD Analysis
While Stop errors can be caused by both PC and software malfunctions, the most common cause is hardware malfunction. Each Stop error is accompanied by a specific error classification and an eight-digit hexadecimal error system. It may not be immediately obvious that you are seeing a BSOD (mainly due to the impact factor that hit you when it occurred), but you can start using the description and code to create your current BSOD. Determine the type of error and that is happening. You just need to be able to understand the key elements of the message in order to have direction and focus on your troubleshooting expedition. This is a trick for finding relevant BSOD information.
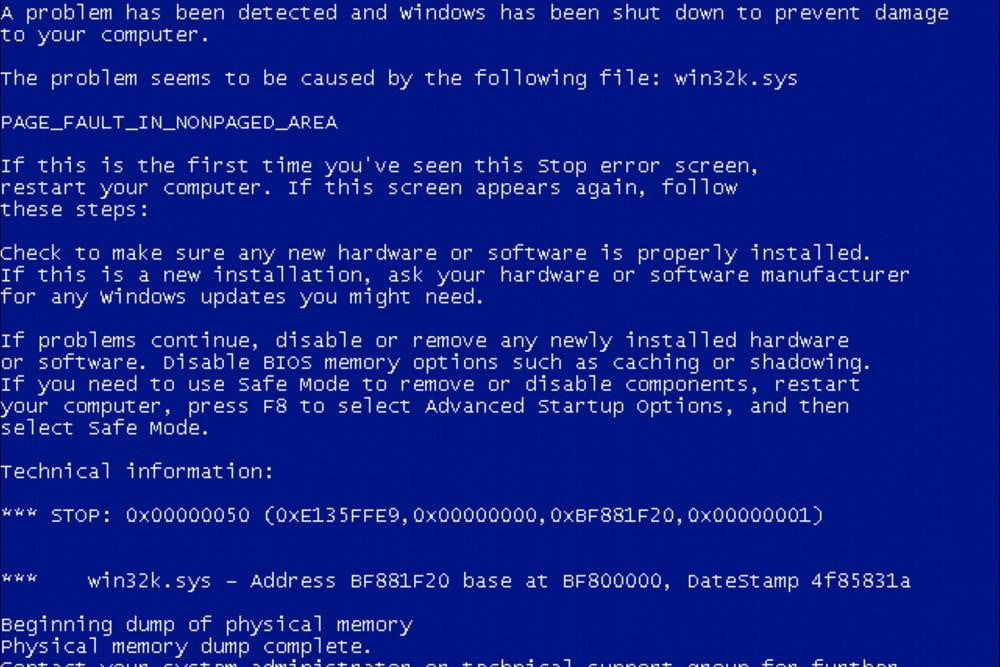
Let’s say you encountered the BSOD in Figure A.
Figure A
 < / h5>
< / h5>
This Stop error indicates that the requested data is not too much in memory.
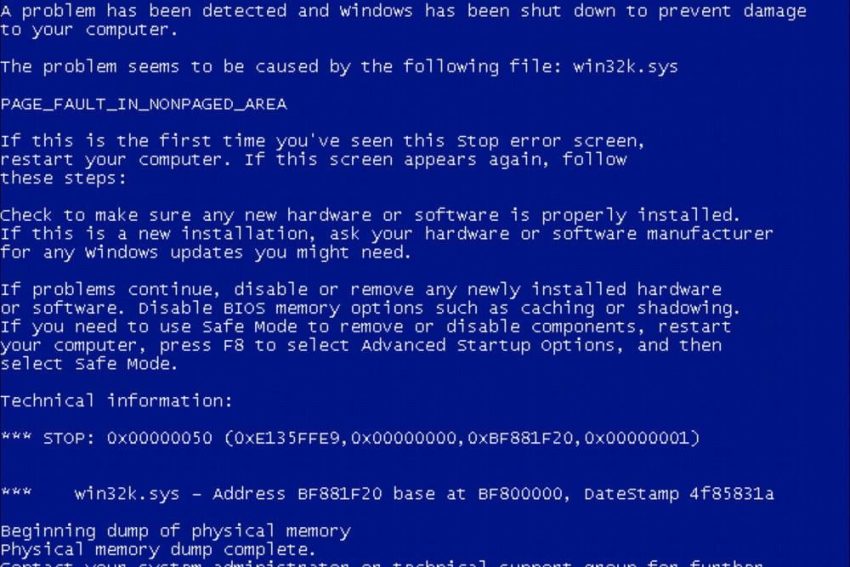
At the top of the Windows XP BSOD is an explanation for an error in which multiple words are capitalized, concatenated with underscores because they contain characters. In the following BSOD snippet, you can see that the text KMODE_EXCEPTION_NOT_HANDLED is a description of the error:
A problem has been detected and Windows has been shut down to prevent damage to the real computer. PAGE_FAULT_IN_NONPAGED_AREA
After describing the error, follow some general troubleshooting steps. In some cases, following these steps will lead you directly to a solution. (Remember, this information appears in almost every BSOD.)
Bthe first time you see this restart error screen, your netbook will be. If this screen reappears, do the following:Check if new software or gardening has been installed correctly. If this is a fresh install, check with your computer system or software manufacturer for which versions of Windows you might need.
If the problems persist, disconnect the newly installed hardware or platform. Disable BIOS storage options such as shadow caching. If you need to use Safe Mode to uninstall or disable products, restart your computer, press f8, select Advanced Boot Options, and then select Safe Mode.
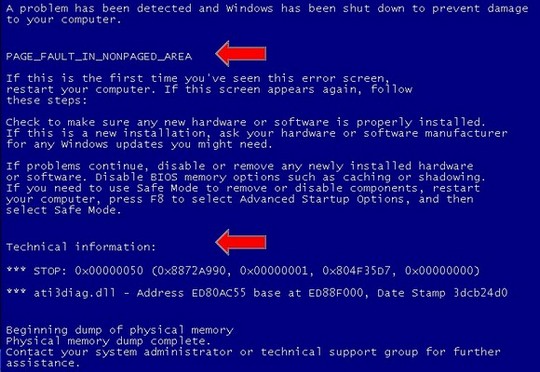
After the general troubleshooting information, you’ll think of the tech section, which contains an eight-digit hexadecimal error code. The rule is usually followed by four sums depending on the error in parentheses. (These values are usually not information, they are necessary, but you should write them down.) If the transmission was direct is related to the problem because it caused the BSOD, it will also be listed here. In this case, you can see that there is a problem in the ati3diag.dll file:
Technical information: *** STOP: 0x00000050 0x0000001, (0x8872a990, 0x804F35D7, 0x00000000) *** ati3diag.dll - ED80AC55 base address for ED88F000, timestamp 3dcb24d0
After the “Technical Information” section, you will find another general section. This informs you that Windows XP has saved the contents of system memory to the correct file on your hard drive:

Starts a backup of the dedicated physical storage. Physical emptying is complete. Contact the technical support service of your system or your administrator for help.
With this information, a person can visit Microsoft’s Help and Support page on the Internet and search the available knowledge base for more detailed solutions and troubleshooting information.
Common BSODs In Windows XP
Now that you have a good understanding of how to parse a good and reliable BSOD and extract relevant information from all the gibberish, let’s take a look atand some related to the most common BSODs in Windows XP. I will only cover a few BSOD conditions, but many of them have possible Stop errors. For every BSOD I talk about, I’ll link to their Microsoft Knowledge Base article about that particular Stop error. (As there may be multiple articles pointing to “Stop this Simple Mistake”, if you find your entire family needs more information, be sure to search my knowledge base.)
This Stop error, which must be caused by software or tools, indicates that a kernel mode or autopilot process tried to access a location that was not allowed access, or possibly a location that exists elsewhere kernel interrupt request. Level (IRQL) that was probably too high. A kernel-mode process can only access other processes whose IRQL is usually equal to or less than its own.
This Stop error indicates that the Windows XP kernel has encountered an invalid or unknown instruction on p designing. The problems causing this Stop error can be hardware or software related and can be related to invalid access violations and memory regions caught by the Windows standard error handler when there are no error handlers in the code itself.
Approved: Fortect
Fortect is the world's most popular and effective PC repair tool. It is trusted by millions of people to keep their systems running fast, smooth, and error-free. With its simple user interface and powerful scanning engine, Fortect quickly finds and fixes a broad range of Windows problems - from system instability and security issues to memory management and performance bottlenecks.

This stop error indicates that the requested data is inconsistent with a memory write. The system throws an exception when a reference to a very invalid system memory address is used. An error in the internal memory (including main memory, L2 cache RAM, video RAM) or incompatible software (including remote management and anti-virus software) can cause this Stop error.
This Stop error indicates that Windows XP lost access to the system partition, boot volume, during the boot process. Installing the wrong device drivers while installing or updating the storage adapter hardware will usually block our error. This error can also indicate almost any possible infectious virus.
This Stop-errorsThis indicates a serious hardware problem caused by memory incompatibility, bad memory, or malfunction.
Speed up your computer's performance now with this simple download.
Safety problems. Many internet marketers have criticized Windows XP for its buffer stream vulnerability and vulnerability to malware such as viruses, Trojans, and worms.
One way to fix Windows XP when the system starts up slowly is to disable annoying and predisgusting Windows XP startup programs. By far the easiest way to temporarily disable the boot disks is to boot the system in Safe Mode, because Windows XP starts with a clean configuration in Safe Mode.
Windows update error 0x80070057. Sometimes a certain Windows error code doesn’t help you.DLL error.Error in the security certificate.Blue screen stop error.Failed to access prohibited folders.