Approved: Fortect
If you see an error while mounting Fat32 partitions on your computer, you need to check these troubleshooting methods.
F. I was fortunate enough to have a dual boot system with Windows XP (FAT32) and Linux Debian. How to access all files from Windows XP FAT31 partition?
A. You can access it using less than the mount command. You need to mount the concept as a vfat section. Supported
Approved: Fortect
Fortect is the world's most popular and effective PC repair tool. It is trusted by millions of people to keep their systems running fast, smooth, and error-free. With its simple user interface and powerful scanning engine, Fortect quickly finds and fixes a broad range of Windows problems - from system instability and security issues to memory management and performance bottlenecks.

See first steps with long file names (LFN). The filesystem style with this change is usually called VFAT, which is the Windows 95 VxD device driver. Fdisk
Use the -l command to get the vfat section name: # fdisk -l
Conclusion:

Then enter a mount command like this which will mount the
partition # mount -t vfat / dev / hda1 / mnt / d
Ubuntu could read and send files stored on Windows formatted partitions. However, partitions that are usually formatted with NTFS are sometimes formatted with FAT32. FAT16 is also displayed on other devices.
Ubuntu displays NTFS / FAT32 files and file systems in hidden Windows directories. As a result, important hidden system files will appear in every Windows C: partition when it is connected. Since it is really too easy to accidentally change or delete important files for Windows, you should mount the Windows partition C: as rarely as possible, preferably not all or read-only by installing / etc / fstab (see below). If you have data that you want to regularly access from Windows and Ubuntu, it is best to create a separate large NTFS data partition.
Regardless of whether you are writing to your C: Windows section or to the general information section NTFS, please note that if you are using Windows 7 and Windows 7 is hibernating while writing, make sure you are using the NTFS partition of Ubuntu, you will lose all your changes. This is because when the system is idle, Windows 7 transmits system state information to a file stored on the hard drive and restores it after this boot when the system is reactivated, freezing the entire file system to its previous state. for any changes made to Ubuntu. Hibernation must be avoided in Windows 7. In Windows 8, the situation is modern because when you turn off the hibernation / shutdown model, a certain hybrid is used by default. Changes made by Ubuntu will be lost when you restart Ubuntu.
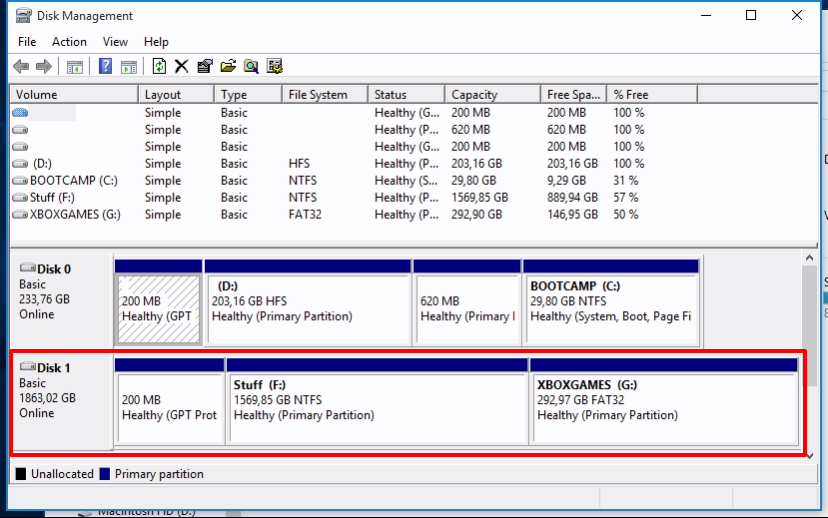
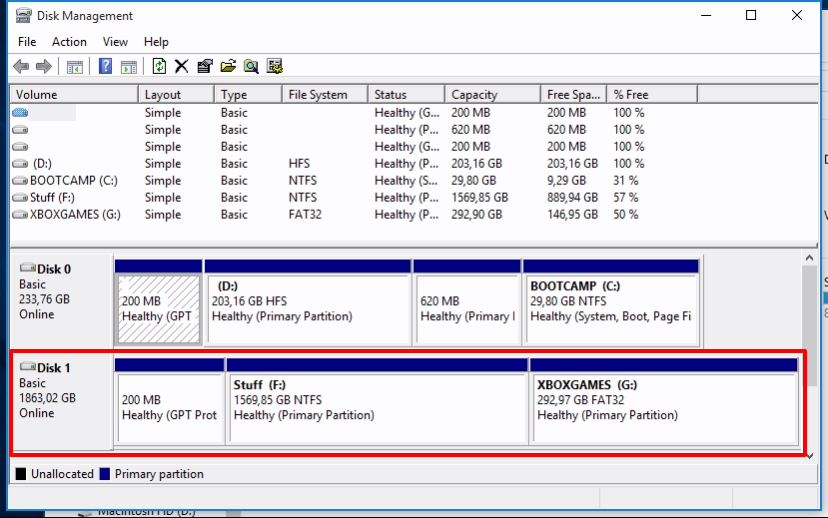
Windows 7 and Windows 10 (when installed over the old mbr partition table) typically have a 100-200 MB partition called “SYSTEM”. Don’t drive this – you don’t have to. It is also highly recommended not to mount many of the recovery partitions.
For those who only use the desktop version of Ubuntu or the version connected to its official productionThe simplest and fastest way to mount NTFS or FAT32 storage spaces is through the file manager: Nautilus in Ubuntu, Thunar in Xubuntu, Dolphin in Kubuntu, and pcmanfm in Lubuntu. Just find the section you want to save in the left pane of the directory and click on it – it should be mountable and its contents will appear in the main area. Sections are displayed with their own tags or tags, otherwise they are displayed with their own size.
If you don’t need a Windows partition – or an NTFS / FAT32 partition to communicate with Windows – every time you log in at every boot for the reasons below, a mount originally done through a file manager in this way might be sufficient.
If you are using the wubi version of Ubuntu and want to view the host partition, you never need to mount it – it is already mounted in the host folder. In the left pane of the Nautilus file browser, click File System, then immediately open the hosts folder, which you should see in the main pane.
For a more detailed and in-depth analysis, see LinuxFilesystemsExplained, plus some basics:
- Windows 7, Vista, XP, 2000, older NT systems like Windows Server 2003 and 2008 are formatted as NTFS. In rare cases, OEMs may pre-install Windows and XP Windows 2000, which will use FAT32 file systems.
- Older versions of Windows such as Windows ME, 98 and 95 may well be formatted as FAT32.
- Flash drives such as a USB stick or digital camera flash drive are usually formatted as FAT16. Some flash drives are formatted using Microsoft’s proprietary exFAT file system.
On Windows, a user can check the file system that this partition is formatted with by right-clicking the partition in Windows Explorer and choosing Properties. On Ubuntu, run from terminal:
-
sudo fdisk -lu
NTFS
The ntfs-3g driver is used on Linux systems to read and write NTFS partitions.
NTFS (New Technology File System) is a file system developed by Microsoft and used by computers (Windows 2007 and above). Prior to Linux 2007, distributions relied on the NTFS kernel driver, which in turn was write protected. EnjoyThe ntfs-3g-Rider space now allows Linux-based systems to read and write NTFS-formatted partitions away from NTFS-formatted partitions.
The ntfs-3g driver is preinstalled in all current versions of Ubuntu, and NTFS error-free detectors should be triggered just before proceeding with the configuration. So, in later releases of Ubuntu 11.10, the ntfs-3g package contained the use previously provided by ntfsprogs. Attempting to download ntfsprogs on October 11 (and possibly April 12) will prompt the package manager in case you want to remove ntfs-3g. Users who installed ntfsprogs and were unable to accidentally take advantage of the package manager message removed ntfs-3g, causing the software to switch to the read-only NTFS kernel driver. The loss of the ntfs-3g driver for similar reasons was also reported on every update from 11.04 to 11.10. If you cannot write to your partition or device in NTFS format, no matter if you have ntfs-3g package or not.
FAT32
The vfat driver is used in Linux to read and write FAT32 and FAT16 partitions.
foreword
If you want to automatically mount one of the Windows partitions at boot time, you need to add another one to include the / etc / fstab file for each partition you mount. Here are some reasons to mount partitions using / etc / fstab instead of using the document manager:
- comfort.
- When multiple men or women use an account during another session. Partitions mounted from User Funding using File Manager are definitely inaccessible to other accounts.
- Where the collections were created in situations like Banshee or Rhythmbox (for music) and Shotw
Speed up your computer's performance now with this simple download.FAT32 format Its only job is to format records to FAT32, and it does it surprisingly well. The FAT32 format works from Windows XP up to 10 and supports partition sizes up to 5TB. You can choose a specific allocation unit size and assign a new volume name to my partition. Unfortunately, he was unable to create new partitions.
Mount the CD.View all frames.Mount all filesystems mentioned in / etc / fstab.Just mount the real filesystem from / etc / fstab.View all partitions mounted under certain types.Mount the floppy disk.The mount link points to the new cat log.
FAT32 is read / write compatible with the latest and most legacy operating systems such as DOS, most flavors of Windows (up to and including 8), Mac OS X, and in addition, many variants of computer systems. Exploitation derived from UNIX such as Linux and FreeBSD.