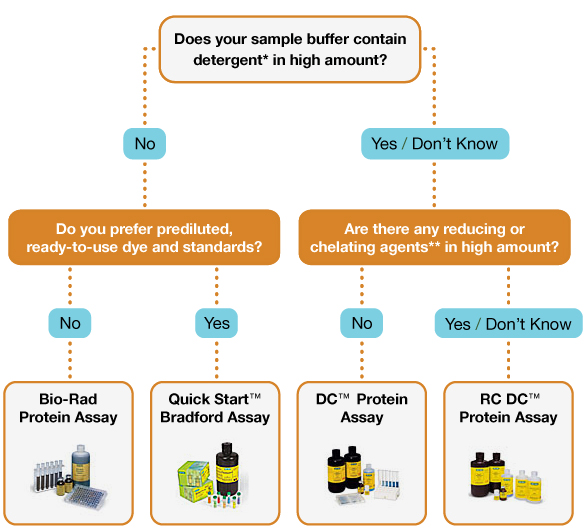
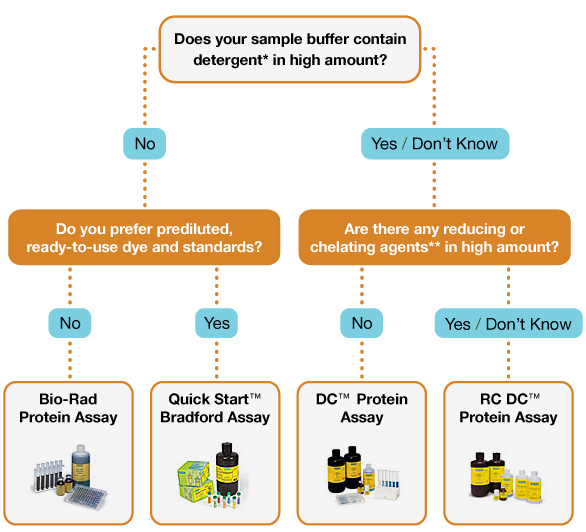
Recently, some of our users have encountered an error code while troubleshooting Bradford Protein Assays. This problem can arise for several reasons. We’ll cover them below.
Approved: Fortect
Chemistry of BCA Protein Assay 15 Benefits of BCA Protein Assay 16 Disadvantages of BCA Protein Assay 17 BCA Protein Assay – Reducer Compatibility 18 BCA Protein Assay 19 Micro BCA Protein Assay 20 Coomassie Dye Protein Assay (Bradford Assay) 21
The Uptake Of The Protein Sample Is Now Lower Than Expected
Absorb Higher Than Expected Healthy Protein Sample
Absorption Of Each Of Our Standards Below Expected
Samples May Be Dark Blue
Precipitation Amount In The Sample
Experiment With Proteins Contains Interfering Substances:
Note. This is not an exhaustive and exhaustive list of compatible substances and their individual concentrations. There are many substances that interact with proteins in different ways. Reagents can alter the pH of the test, which will affect the correct performance of the Bradford test.
Technical Advice
Bradford Protein Assay is a simple and easy way to quantify protein concentration if needed, but sometimes troubleshooting may be required.
The dye binds to both basic and aromatic amino acids, causing a change in absorption. It is easily recognized by its color change from brown to blue. Your protein concentrate can be determined using standard proteins, mainly BSA (bovine serum albumin).
factors such as; Heat, wavelength, detergents and even usedFancy cuvettes can influence statistics and give incorrect results. If you are having some of these problems, don’t worry! This ZAGENO troubleshooting guide will help you!
Below is a summary of the typical problems encountered when performing the Bradford Amino Assay Test.
-
Low molecular weight: The detection limit for our own Bradford test is 3,000 to 5,000 daltons. If the protein is less, use a different quantification method, for example. Table 1). Dilute the protein sample. Make sure your standards are diluted in the same buffer.
-
You have an incredibly high concentration of protein. Dilute the protein sample and measure the protein concentration again.
-
Interfering substances: In practice, interfering substances such as liquids are included (Table 1). Dilute the protein sample. Make sure your standards are diluted with the same buffer.
-
Colored reagents are too old, not stored properly: Bradford’s reagent has a shelf life of approximately 12 times a year. When it gets old, replace it with rasshsterile and store at 4 ° C.
-
Standard dilutions instead of properly prepared: follow the manufacturer’s instructions to accompany the protocol that creates your standard protein dilutions.
Approved: Fortect
Fortect is the world's most popular and effective PC repair tool. It is trusted by millions of people to keep their systems running fast, smooth, and error-free. With its simple user interface and powerful scanning engine, Fortect quickly finds and fixes a broad range of Windows problems - from system instability and security issues to memory management and performance bottlenecks.
- 1. Download Fortect and install it on your computer
- 2. Launch the program and click "Scan"
- 3. Click "Repair" to fix any issues that are found

Dye reagent too cold: Bring Bradford’s reagent to room temperature before starting analysis.Absorbance measured at the wrong wavelength: Measure the total absorbance at 595 nm.
-
High alkaline concentrations: this increases the pH value above the limit value of Bradford’s reagent. Dilute or dialyze sample
-
Detergents During Protein Buffer: Dialyze the required sample or dilute it to reduce this particular level of detergent.
Interfering substances in charge 1 are one of the main problems when performing the Bradford test. Table 1 provides a list of the most commonly used substances and their permissible concentrations. Please refer to the manufacturer’s standard protocol for the described information. If a substance you are taking is considered incompatiblewith concentration or not calculated at all, see section below.
-
The concentration of the interfering substance does not match the Bradford test: if you have a high protein concentration, dilute the sample to the point where there will be no interference, or remove the substance on dialysis

Substance may not be on the reagent compatibility list: run two standard curves, one with the best protein in your buffer, the other with your own protein in water, and plot the protein concentration versus absorption. If the actual shim does not interfere with your size, I would say the two standard curves have the same slope.
Table 1. Concentrations of compatible substances in the Bradford-Type test (2012))
-
The dye reagent can work with quartz cuvettes; It is best to use glass or plastic cuvettes.
-
Dirt on the glassware can affect your measurements, so of course you must clean it before use.
-
The temperature of the Bradford reagent must match the temperature in the cabin

Speed up your computer's performance now with this simple download.
– Two potential problems with the Bradford test is that the test is often only effective for larger proteins, and the sample must be within a specific temperature and pH range. Samples containing the required proteins below 3000-5000 Daltons are difficult to read due to the absorption being too low.
Unlike other health tests, the Bradford protein test is less sensitive to the effects of various chemical compounds such as sodium, potassium, or even carbohydrate-like sucrose, which may be present in the amounts required for protein. Exceptions are excessive concentrations of detergent.
Multiple concentrations of the main unknown sample can be used to improve accuracy. Add 100 μl of diluted Bradford reagent to all wells. Total inflation is 200 μl / well. Wait at least significant minutes, but no more than 60 minutes, for the color to develop.