In this guide, we’ll find out some of the possible causes that Windows Task Manager might start, and then we’ll point out possible recovery methods that you can try to fix the problem.
Approved: Fortect
Performance (Memory) Tab The next hardware category on the Performance tab of Task Manager is Memory, Advanced, and Reports for various aspects of newly installed memory. Above the top graph, you can see the total memory, ad Recorded in GB, installed and recognized by Windows.
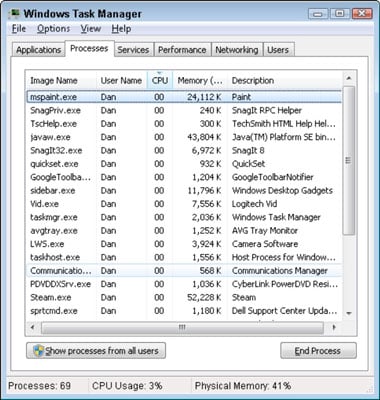
The Windows Task Manager is definitely a powerful tool that collects useful information about the overall use of system resources so that you can get detailed statistics for each process. This book covers all features and technical terms in Task Manager only.
Approved: Fortect
Fortect is the world's most popular and effective PC repair tool. It is trusted by millions of people to keep their systems running fast, smooth, and error-free. With its simple user interface and powerful scanning engine, Fortect quickly finds and fixes a broad range of Windows problems - from system instability and security issues to memory management and performance bottlenecks.

This article focuses onI use Windows 10’s Task Manager, although many of them also apply to Windows 7. Microsoft has kept a significantly improved Task Manager since Windows 7 started.
How to start the task manager
Windows provides many ways to start the Task Manager. Press Ctrl + Shift + Esc to open Task Manager using the magic keyboard, or right-click on the Windows taskbar and select Task Manager.
What do you need to know about the task manager?
The Task Manager is a component of the operating system that is present in all versions of Microsoft Windows for Windows NT 4.0 and Windows 2000. It allows the user to see who is currently running on the system, each process, and the performance of the global computer. How to free Windows Task Manager.
You can also press Ctrl + Alt + Delete, then click Task Manager from any of our screens, or search for the Task Manager shortcut in the menu launcher.
Simple view
When you first introduce Task Manager, you will see a simple and unassuming window. This window lists the applications running on your desktop, excluding background software packages. Here you can select an application or click Task to close it. This is useful when the usage is unresponsive – in other words, it’s frozen – and your business can’t shut it down normally.
The Task Manager is a component of the operating system that can be found on all devices running the Microsoft Windows platform. It provides information about how and how applications, processes and services work, computer performance, network activity, and storage information.
You alsoyou can right-click the application in this window to access additional options:
- Switch to: switch to any application window, optimally transfer it to the desktop and set it using focus. This is useful if you are not sure which window applies to which loan application.
- End of task: End the process. It works the same as a button to complete a task.
- Run the task again: open a new task “Create windshield” where you can specify the address of a program, file, document or website, and Windows will open it.
- Always On Top: Make the Task Manager window itself “always on top” that links to other windows on your desktop so your company can see it at any time.
- File Location: Open the file in an Explorer window, which displays the complete location of the program’s EXE file.
- on the web: Search for Bing by task name and program file name. This will definitely help you see what the program is now and what it does.
- Properties: Open the properties window of the program’s .exe file. Here you can optimize the compatibility settings and, for example, check the version number of the program.
Find
When Task Manager is open, you will see a single Task Manager icon in your notification target. Tells you how much central processing unit (CPU) resources are running on your system, and you can hover over it to see memory, disk, and then network usage. This is an easy way to track your computer’s CPU usage.
To see the icon on the taskbar without showing the Task Manager in the notification area, click Options> Hide On Minimization in the full Task Manager specific interface and minimize the Task Manager window.
Description of Task Manager Tabs
To see a lot of additional tools in Task Manager, click More in the Simple Viewer. You will see a complete tabbed interface. The task manager will also open up your reminder settings for more complex visits in the future. If you want to come backto simple view, click “Less details”.
What is the name of the Windows Task Manager?
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia’s Task Manager, formerly known as Windows Task Manager, can be the Task Manager, System Monitor, and Startup Manager included with Microsoft Windows systems.
When “More” is selected, the Task Manager contains the following tabs:
- Processes: The specified execution of background applications and processes associated with your system, as well as CPU, memory, CD, network, GPU, and other resource consumption information.
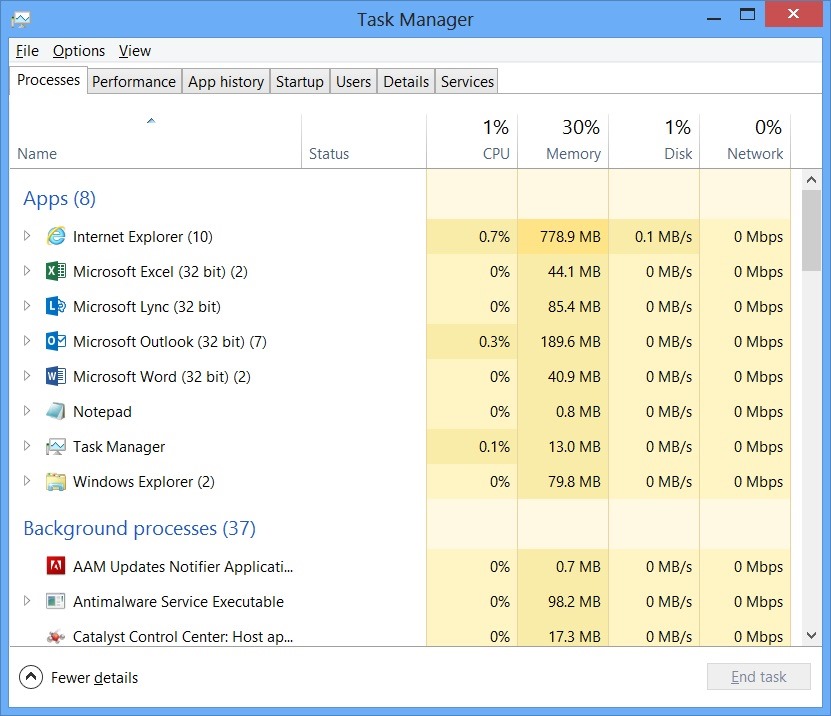
- Performance: Real-time graphs showing the total utilization of CPU, memory, primary, network and GPU resources for your device. You can also find many other details on this site. From your computer’s IP address, you can model the names of your computer’s CPU and GPU.
- Application History: Information about the number of processors and resources that network applications have used for your current account. This only applies to new Universal Windows Platform (UWP) apps – in other words, store apps – and far from traditional Windows desktop (Win32) apps.
- Startup: a selection list of your startup programs, that is, applications that Windows startsAutomatically when you log into your user account with their name. From here you can turn off the startup programs, although you will definitely do this through Settings> Applications> Startup.
- Users: User accounts that are currently stored on your computer, how much money they use, and what applications they run.
- Details: More detailed information about the processes running on the new system. This is mainly the Processes tab of the Task Manager in Windows 7.
- Services: Administration of system services. This is the same information you can find in services.msc, the service management console.
Control aria-level = “2” role = “heading”> 

When Task Manager is open, you should see the Task Manager icon in this notification area. This will show you how much central processing unit (CPU) resources are undoubtedly being used on your system, and anyone can hover over to see memory, disk and network usage. This is a handy way to keep track of your personal processor usage.
The Processes tab displays a complete list of processes running on your system. If you name it, then the list should be divided into three categories. Apps Corporation displays the same list of running tools The items are the same as in the “Abbreviated Information” view. The other two categories are native and Windows processes and event processes that are not in the simple simplified view of Task Manager.
For example, tools like Dropbox, your antivirus, background updates, hardware, and utilities will show up with icons for the notification environment (on the taskbar) in a list of activities in the background. Windows processes include various processes that are part of the Windows operating system, although some of them go through “background processes” for some reason.
You have the option to right-click a process to see what action you can take. You can see the options where the context menu is located:
- Expand. In some applications, such as Google Chrome, multiple processes are grouped here. Other tools have multiple windows that are part of a single process. You can define the extension by double-clicking or Processes by clicking the left arrow to display the entire group that is being processed Runs processes separately. This option is just
 Speed up your computer's performance now with this simple download.
Speed up your computer's performance now with this simple download.


