Approved: Fortect
Hope that if you have the Windows 7 Login Failed Event ID on your system, this user guide can help you. Event 4625 applies to each of our following operating systems: Windows Server 2008 R2 and Windows 7, Windows Server 2012 R2 and Windows 8.1, and Windows Server 2016 and Windows 10. Corresponding events in Windows Server 2003 and earlier include 529, 530 , 531, 532, 533, 534, 535, 536, 537 and still 539 for login failures. Event ID 4625 is slightly different in Windows Server 2008, 2012, and 2016.
Presentation
Approved: Fortect
Fortect is the world's most popular and effective PC repair tool. It is trusted by millions of people to keep their systems running fast, smooth, and error-free. With its simple user interface and powerful scanning engine, Fortect quickly finds and fixes a broad range of Windows problems - from system instability and security issues to memory management and performance bottlenecks.

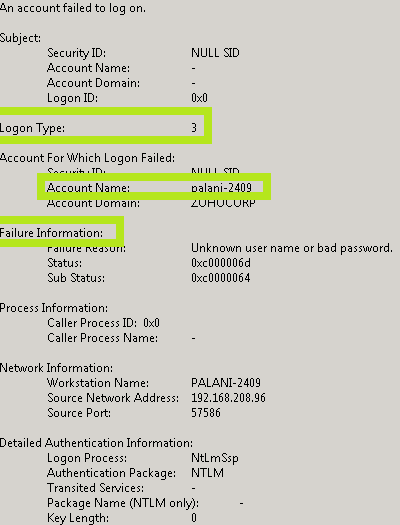
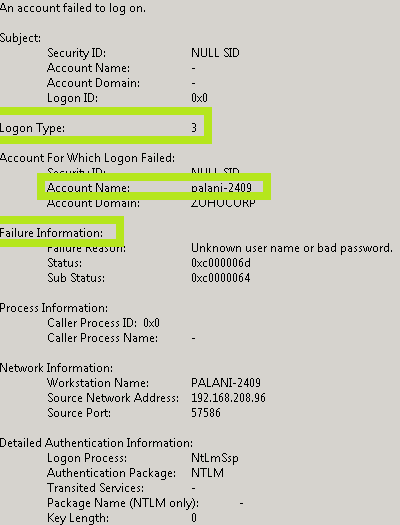
Event ID 4625 (displayed in Windows Event Viewer) documents any failure when connecting to the local computer. This generated event resides on the home PC from which the connection was attempted. A related event, Event ID 4624, documents successful connections.
Event 4625 applies to systems: After starting Windows Server 2008 R2 and Windows 7, Windows Server 2012 R2 and Windows 8.1, and Windows Server 2016 and Windows 10. Corresponding periods in Windows Server 2003 and earlier include 529, 530 , 531, 532, 533, 534, 535, 536, 537 were unsuccessful and 539 were for registration.
Event ID 4625 is slightly different from Windows Server 2008, 2012, and 2016. The screenshots below highlight the major areas of each of these versions.
Description Of Event Fields
- … Connection type: This field indicates the type of connection that should have been made. In other words, it shows how your user tried to log in. There are nine different types of entries. Any connection type other than 5 (which indicates a high runlevel) is marked with a red flag. For a description of the different connection types, see event ID 4624.
- • Account for which logon failed: This section displays the name of the account of the user who tried to log on.
- … Error Information: This section explains the reasons for each of our connection errors. Floorf “Cause of Error” contains a short explanation, while the “Status” and “Subwoofer Status” fields contain hexadecimal codes. The most common ones are also described below.
- … The domain displays the account of the closest system that requested the connection (not the user).
- … The Process Information section displays detailed information about the process that no doubt tried to connect.
- … The “Network Information” section shows where the user was when he tried to connect. If the connection was initiated from your current desktop computer, this information is either blank and also includes the local computer workstation name and network address.
- … The Verbose Authentication section contains information about the certification package that was used when trying to connect.
A user who did not receive the requested login type on this computer. To
Reasons For Tracking Ix CrashesEntering The System:
To detect brute force, dictionary attacks, and other password speed attacks, which are here marked by a sudden increase in failed login attempts.
To detect abnormal and potentially harmful internal activities, eg. For example, trying to log on with a disabled account or unauthorized workstation, users log on outside of business hours, etc.
To improve it by adding a link to the System Setting Account Lockout Threshold, which determines the number of failed login attempts from the number of login attempts before the user account is locked out.
Accurate logon error information is indeed required by government regulations.
Need For A Third-party Tool
In a typical IT environment, there are thousands of events with ID 4625 (login failure) every day. Connection failures are useful when using them, but a better understanding of the network activity of computers can be gleaned fromconnections between them and other relevant events.
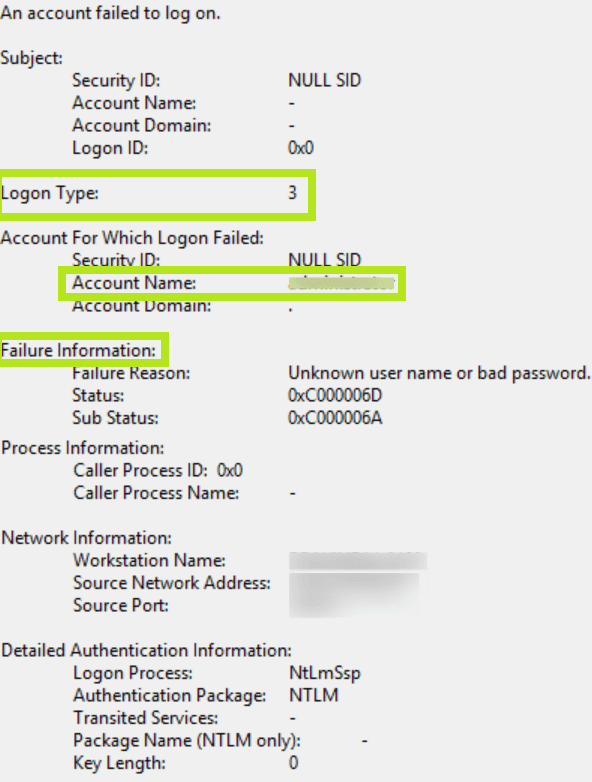
For example, although event 4625 is generated when the best account cannot connect, and event 4624 is generated for successful connections, neither of these events indicate whether the same account was recently known by both. To figure this out, you will need to match event 4625 with the appropriate login credentials through event 4624.
Thus, event analysis is correlated and necessary on the road to implementation. Native PowerShell tools and scripts take understanding and time to use to the fullest. Therefore, a third party tool is really necessary.
Using machine learning, ADAudit Plus creates a user-specific action base and only explains to security personnel if there are any deviations from this standard.
For example, a user who usually has constant access to an important server outside of business hours will not trigger a false alert, as this is typical behavior.user. On the other hand, ADAudit Plus will immediately alert security personnel because the same user is accessing this server at a time they have never accessed before, even if access falls during hours of anxiety.
Speed up your computer's performance now with this simple download.