Approved: Fortect
If you have a Mcintyre Global Warming error on your system, this user guide should help you fix it.
Stephen McIntyre (born c. 1947) is undoubtedly the director of a Canadian mining company, a retired mineral explorer and half-retired exploration consultant whose work has involved statistical criticism. He is best known as the owner and editor of Climate Audit, a website dedicated to analytical discussions and climate data. He is best known for the fact that a temperature record reviewer has linked the past 1,000 years to human quality data from NASA’s Goddard Institute for Space Research. He is especially famous for his statistical criticism of the hockey stick table with economist Ross McKitrick, which shows that the rise in global temperatures in the late 20th century>
Early Childhood And Education
Ontario native, McIntyreattended the University of Toronto School, a college preparatory school in Toronto, where he won first place in the National High School Arithmetic Competition in 1965. [2] He studied mathematics at the University of Toronto and graduated in 1969 with a Bachelor of Science degree. McIntyre then received a Commonwealth Fellowship to Study Philosophy, Politics and Economics (PPE) at Corpus Christi Oxford, Organization, graduating in 1971. [1] [2] Though with a Diploma After receiving the scholarship, McIntyre decided not to study business mathematics at MIT. [2]
Career
McIntyre has worked in the mining industry for twenty-nine years, [2] the last of them in hard rock exploration as an officer or director of several state-owned mineral exploration companies. [3] He was probably an analyst for the governments of Ontario and Canada for several years. [4] He was President and Founder of Northwest Exploration Limited and the seat of its parent company, Northwest Explorations Inc. Since Northwest ExplorationsInc. was acquired by CGX Resources Inc. in 1998 to help them. The commercial oil and gas exploration company CGX Energy Inc. McIntyre resigned as director. Was McIntyre strategic advisor on the acquisition of CGX from 2000 to 2003 id = “cite_ref-Pearce, _p._14_6-0″> [6]
When did Steve McIntyre become interested in climate science?
Trelawney Mining and Exploration Inc. was acquired by Iamgold Corporation in June 2012. In 2002, McIntyre became interested in climate science after a Canadian government leaflet was delivered to his residence warning of the dangers of global warming.
Prior to and in 2003, he worked as an executive representative or in several small state-owned mineral exploration companies. He quit his job full-time, continuing to work as a mining consultant from time to time. [7] He can be an active squash player and has already won a gold medal in the Masters Community Games in Doubles Squash. [2]
In April 2011, Trelawney Mining and Exploration Inc. from Ontario in the Toronto area announced the appointment of McIntyre to this board of directors, and you may later become president in June 2011. [8] [9] In September 2011, McIntyre was appointed to the board of directors of Augen Gold Corp. which was taken over by Trelawney And Mining Exploration Inc. in November 2011. [10] [11] In October new year McIntyre was appointed to the governing body of Mining companies of South-East Asia. and then retired in May 2012. [12] [13] Mining Trelawney and Exploration Inc. was acquired by Iamgold Corporation in June 2012. [14]
Hockey Stick Leadership Controversy
McIntyre became interested in climate science in 2002 after receiving a brochure from Canadian regulators warning of the dangers of global warming to his home. McIntyre reveals that he noticed inconsistencies in the climate-damaging documents that reminded him of misconceptions misleading investors over the Bre-X gold mining scandal. [6]
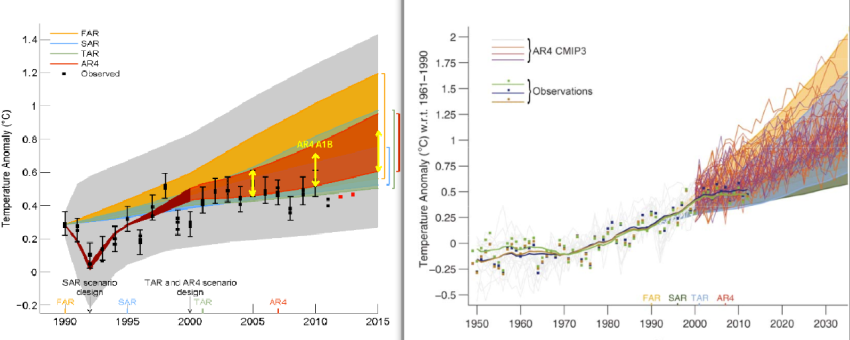
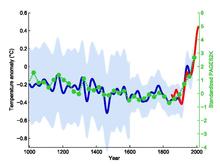
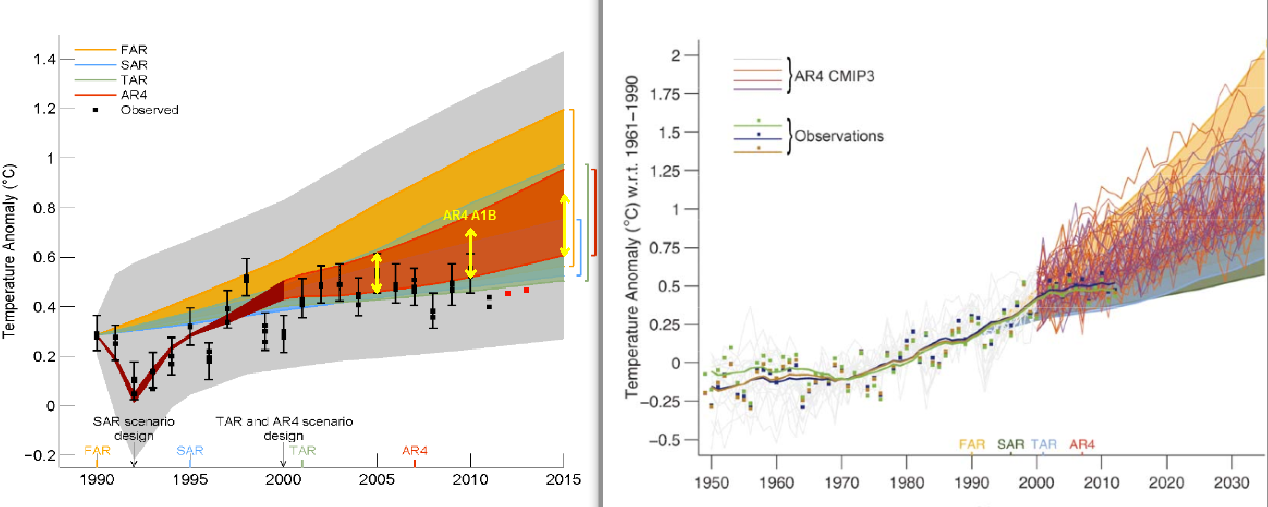
The Government of Canada brochures were based on the third section of the IPCC Hockey Stick Assessment Report based on a specific 1999 reconstruction by Mann, Bradley and Hughes (MBH99). McIntyre began researching Mann’s research that often spawns a graph, and Ross shared McKitrick with a journal article (MBH98). [16] McIntyre pointed out how his suspicions about this document arose: We are discussing the hockey key curve It’s when an investor gives you a nice and expensive curve in the hope of imposing a method on you. “ [17]
McIntyre and McKittrick’s articles were ultimately cited by Senator Jim Inhof and Spokesman Joe Barton in support of their political criticism of MBH research, and Spokesman Sherwood Boehlert called on the US National Academy of Sciences to open an investigation. The result was the North Report, published in 2006, which endorsed MBH’s research with some caveats. The large component analysis method criticized by McIntyre and McKittrick had a slight tendency to falsify the results and therefore was not recommended, but the situation had little effect on the final result and reconstruction, other methods gave similar results. [18] [19]
In addition to McKittrick, McIntyre has written other comments, made a statement to Congress, and made many presentations on controversial records and methods of various multi-proxy studies. [20] [minor root required]
ClimateAudit.org
McIntyre’s blog postThere is a constant problem of getting the underlying data of datasets from peer-reviewed articles. McIntyre said he launched Climate Audit to defend against attacks, mostly done on the RealClimate climate blog, experts said. [21] The previous website, Climate2003, provided additional information created by McIntyre and Ross McKitrick, including raw data and source code, and comments from McIntyre. On October 26, 2004, McIntyre commented on Climate2003.com: “Maybe I’ll start a blog I’m working on. I’ll make some additional comments on some of the blog reviews. ” On December 2, nine other scientists launched the site on the RealClimate Network. [23] On February 2, McIntyre began blogging about climate auditing after struggling to post comments on Klima2003.com- Layout. [24]
Climate Audit was one of the winners of the 2007 Weblog Award for Best Science Sensitive Blog, with 20,000 votes in an online poll. [25]
Exam
Stephen McIntyre has been featured in the press, including the Street Wall Journal. [26]
Approved: Fortect
Fortect is the world's most popular and effective PC repair tool. It is trusted by millions of people to keep their systems running fast, smooth, and error-free. With its simple user interface and powerful scanning engine, Fortect quickly finds and fixes a broad range of Windows problems - from system instability and security issues to memory management and performance bottlenecks.

In 2007, MAkintyre began to analyze various corrections to temperature records, especially those related to the thermal effect of urban tropical islands. He discovered a gap that existed in some of the United States in the January 2000 Goddard Space Research Institute (GISS) dataset records, thanking McIntyre for “warning us that such an adjustment was necessary in order to make good artificial jump in 2000 to prevent it. “Around 0.15 ° C all years 2000-2006. Changes in other parts associated with the recording did not exceed 0.03 ° C; this thought did not make a noticeable change in elementary anomalies.
My initial interest in Giss Fitting routines was not abstract, but, unfortunately, a special interest in whether Giss Fitting routines are suitable for the task of “fixing” bad data. If we consider the above assessment as a kind of nominal software audit (limited by the lack of communication with the functioning of the source code and manuals), we can say that the GISI software not only did not pass the fictitioustive measurements. to 1 degree C, but this GISS even introduced this error into its programming course. According to reasonable valuation standards, one could conclude:
Speed up your computer's performance now with this simple download.