Approved: Fortect
If you have mrouter error on your system, this guide will help you fix it.
Hope this article helps everyone. If you use the tag in a component that does not contain some of the imported elements, this error can occur. Try adding the browser router from “react-router-dom” using your component router. Wrap all the components of the router, then you can include the Link in your components.
Presentation
This document describes a completely common problem that occurs when configuring a multicast application for the first few attempts on a Cisco Catalyst switch network so that multicast does not work. During collection, some servers / applications that use multicast for packages will not be able to run the cluster / high availability process unless you configure the buttons appropriately. The document certainly touches on this topic as.
Requirements
Requirements
Components Used
Information in this document is based on the following PC software and hardware versions:
-
IGMP Snooping. If not, the IGMP / MLD snooping querier maintains a Layer 2 multicast blog that includes snooping switches including a multicast router. For example, if the multicast content is served by a local device, but the router (if applicable) on your network does not support multicast.
Catalyst 6500 with Supervisor Engine 720 running Cisco IOS® Software Release 12.2 (18) SXD5
-
Catalyst runs 3750 , you only have Cisco IOS Software Release 12.2 (25) SEB2 image
Where can I Find my router error code?
05/25/2007 19:33 05/25/2007 19:33 Hi, I am trying to find one of the error codes for my router, but I cannot find the following manual. Can someone tell me how to find such a jar? ICM CallRouter error code. For information on the specific router error code, see the Error Messages section of the *** ICM Master *** Help.
The information in this document was obtained using devices from a dedicated environmental laboratory. All devices used in this document were started with a remote configuration (default). If your network works, try to make sure you understand the potential implications of each command.
Related Products
This document can also be used with the following hardware and software versions:
-
Any Catalyst switch with a Cisco IOS software release that supports IGMP snooping
For more information, see the separate section on the IGMP Support Matrix Monitoring Feature for Catalyst Switches Document the Catalyst Multicast Switch Support Matrix to identify these switches.
Conventions
What is the mrouter port in Cisco VLAN?
Mrouter Deliver is the port that accepts PIM Hello or Join packets and is used to forward all multicast packets. Please take a look at your final vlan to find out who the IGMP Qurier really is. If there is no Qurier, you can simply turn off monitoring or nbuild one Qurier.
This section provides Cisco technical tips forfor more information about document conventions.
Problem
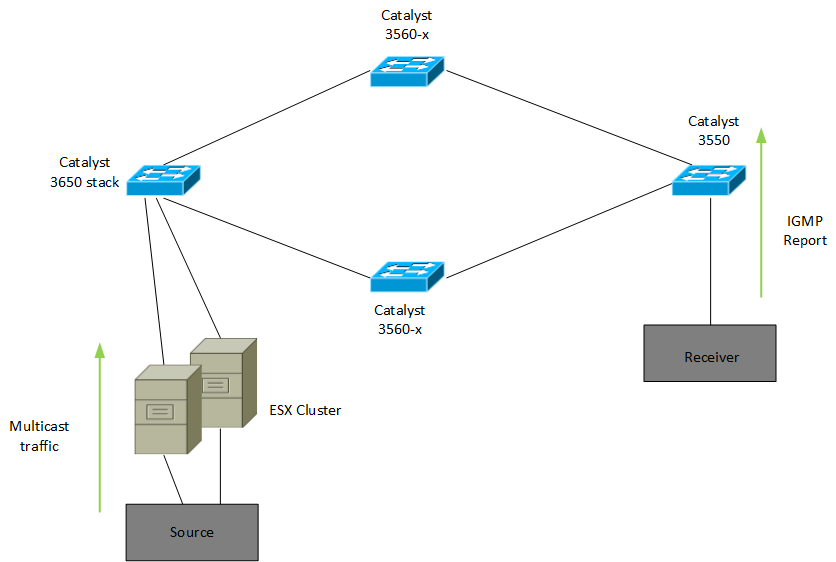
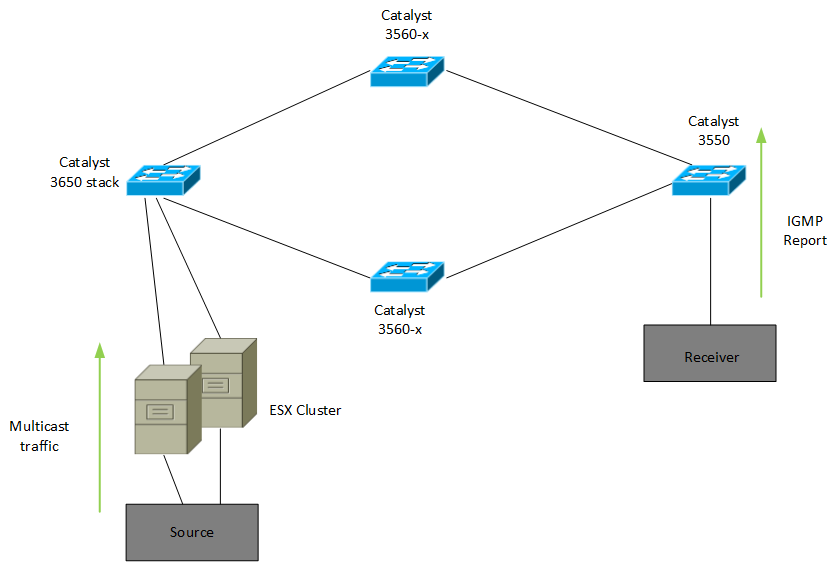
Multicast traffic is not tested on Catalyst switches, even on a shared VLAN. Figure 1 shows a repeating scenario:
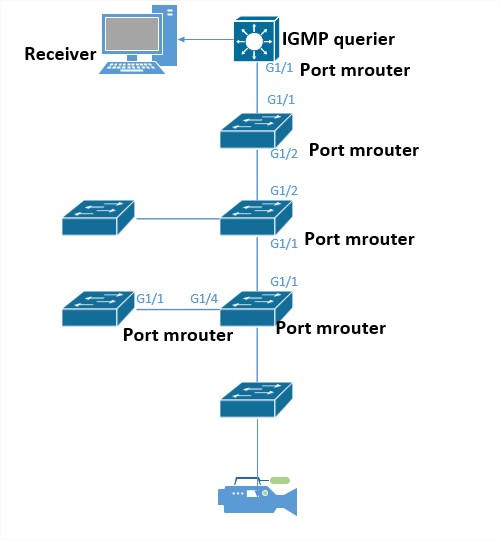
Figure 1. Multicast network configuration with source and destination
The port of a multicast router (mrouter) is usually the port that connects to a multicast router. This is so that multicast routers can in turn start multicast streams and forward registration messages to other subnets.
Multicast start is connected to Switch 1, a Catalyst 6500 switch with a Supervisor Engine 720 running Cisco IOS Software. Receiver 1 is connected to switch and Receiver 2 is connected to switch 2. Switch 2 is the Catalyst 3750. There is a Layer 2 link between Switch 1, let alone Switch 2, regardless of “access or trunk”.
Approved: Fortect
Fortect is the world's most popular and effective PC repair tool. It is trusted by millions of people to keep their systems running fast, smooth, and error-free. With its simple user interface and powerful scanning engine, Fortect quickly finds and fixes a broad range of Windows problems - from system instability and security issues to memory management and performance bottlenecks.

In this process setup, you will see that recipient 1 and this one are on the same switch as any source that accepts a multicast stream without issue. However, sink 2 does not receive multicast traffic. This document aims to really address this issue.
Review Some Important Concepts For M gridding
Before investigating a specific solution and the various options you may come across, you should understand some of the key concepts of Layer 2 multicast. This element defines those concepts.
Note. This section contains a very simple and straightforward explanation for this type of problem only. For a more detailed explanation of these terms, see the Related Information section of this document.
IGMP
is an
igmp is a protocol that allows end hosts (receivers) to notify a multicast switch (IGMP interrogator) of the destination of an end host to receive specific multicast data traffic. So this is a protocol that works between some kind of router and end hosts and allows:
-
Routers query end hosts in case they need some multicast move (IGMP query)
-
End-nodes must finally notify or respond to the router if they are looking for any type of multicastflow (IGMP reports)
IGMP Spy
IGMP Sneaking is a mechanism to restrict multicast data traffic to only the ports to which the listeners are connected. This mechanism improves efficiency because it allows a Layer 2 switch to selectively send multicast packets to the ports that need them. Without IGMP snooping, the switch sends affected packets to every port. Switch “lists” for a specific IGMP message exchange between the hub and end hosts. In this case, the switch creates IGMP, a spy bed that contains a list of all mapped ports that have requested a large number of multicast groups.
Mrouter Port
From the point of view of a switch, a vent mrouter is simply a port that establishes a multicast connection to a router. Having at least one mrouter port is extremely important for IGMP snooping to work on switches. The Understanding the Problem section of this document discusses this requirement in more detail along with the solutions.
MultiadreSmooth L2 Transfer
Every IP version # 4 (IPv4) with data traffic from the destination IP between 224.0.0.0 and 239.255.255.255 will be a multicast stream. All IPv4 multicast packets are assigned a predefined IEEE MAC coverage in the format 01.00.5e.xx.xx.xx.
Note: IGMP
Monitoring only works if a multicast MAC address is assigned to our IEEE compliant MAC zone. Certain reserved multicast strains are excluded from the espionage scheme. If an invalid multicast packet is received on the switched network, the packet is considered flooded on the entire VLAN, which means it is treated as broadcast traffic.
Understanding The Problem And Its Solution
Guilt,
When IGMP snooping is enabled, the device monitors IGMP visits on the network and again uses this knowledge only to actually forward multicast traffic to downstream interfaces that are connected as a path to interested recipients.
IGMP snooping is enabled on Catalyst switches. With IGMP snooping, your spies switch (or listen to) IGMP messages on all ports. The switch creates 1 IGMP snooping table which is essentially assigned for each multicast group to all of the switch locations it requests.
Suppose that without prior settingRecipient 1 and Recipient 2 have indicated most of their intentions to receive multicast stream 239 239 239. This 239 is assigned to L2 multicast MAC address 01.00.5e.6f .ef. ef. Both Single Switch and Switch 2 create an entry in their watch tables for these recipients in response to IGMP reports, which are typically generated by the recipients. Switch 1 shows Gigabit Ethernet port 2/48 in its table, and Switch 2 shows Fast Ethernet port 1/0/47 in its table.
About this note: At this point, the multicast source hasn’t started working yet.
Speed up your computer's performance now with this simple download.How do you troubleshoot a multicast issue?
Should I enable IGMP snooping?