In some cases, your computer may display an error indicating a squared error function. This problem can be caused by several reasons.
Approved: Fortect
The rmse () function, available for the metrics package in R, is used to calculate the average amortization error between actual values and predicted ideas. forecast: A predicted numeric vector, where each element of a particular vector is a prediction for the associated element in reality.
What Is The Root Mean Square Error (RMSE)?
Approved: Fortect
Fortect is the world's most popular and effective PC repair tool. It is trusted by millions of people to keep their systems running fast, smooth, and error-free. With its simple user interface and powerful scanning engine, Fortect quickly finds and fixes a broad range of Windows problems - from system instability and security issues to memory management and performance bottlenecks.

Remainssmiling in a point cloud. Image: nws.noaa.Clear = “left”> Root gov
Watch the video A quick tour of RMSE and how to use the formula:
Squaring some remainder, averaging the squares, and extracting the square root gives the corresponding root mean square error. Then you use the rms value. The error based on this is a measure of the spread of most y-values around the predicted n-value. Square the residuals, take the average, and then take the square root to find the effective value. Many bugs fixed.
Don’t see the tutorial videos? Click here.
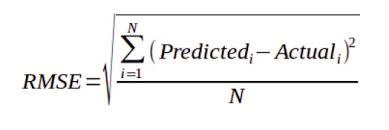
Formula:
Where:
- f forecast = (expected values or unknown results)
- o matches observed values (known results).
The aforementioned lane is in The two squared differences represent the mean (similar to the market xÌ “). Indeed, the same formula can be written with the following slightly different note (Barnston, 1992):
- Î £ = summation (“add”)
- (z f i – Z o i ) 2 = differences , squared
- N = hear greatness.
You can use any formula you like, since both functions do the same thing. For example, if you are not using formulas, you can find Author:
- Square the remainder.
- Find the average of my residuals.
- Extract the square root of the result.
This explains that it can represent many calculations depending on the size of your data. Shortcut to find the main central square:
Where SD y norm is deviation from Y.
If standardized and observational forecasts are used as RMSE information ah, there is a direct relationship with their correlation coefficient. For example, if the effect coefficient is 1, the RMSE will display as 0 because all points are an excuse on the regression line (and there are no errors).
Links
Barnston, A. (1992). “Compliance with the new correlation criteria [root mean square error], as well as the Heidke test; Clarification of Heidke’s score. Notes – and correspondence, Climate Analysis Center. Available here.
Kenny, J.F. and Keeping, E.S. Root Mean Square. 1, 3. Male powerlessness. Princeton, Van nj: Nostrand, pp. 59-60, 1962.
————————————————– —————————————-
We can find the total size of all these oshibok, taking the RMS size for them: √ (error 1) 2+ (error 2) 2 + ⋯ + (error textn) 2n (error 2) 2 + (error 8) 2 + ⋯ + (error textn) 2 n … These calculations give the RMS error of all the regression lines, which tells us how many points are most likely above or below the lines.
Need a discussion with homework? Chegg Study gives you step-by-step answers to your questions from an experienced professional. Your first 30 internships at Chegg Tutor are free!
comments? Want to post a fix? Please leave a comment on our Facebook page.
What Is Root Mean Square Error (RMSE)?
Root mean square error (RMSE) is the generalized deviation of residuals (prediction errors). Residues are a measure of the distance between all and data points of linear regression; The RMSE is a measure of the extent to which these residues are spread. In other words, the game shows how well the data is centered around the line of best fit. The root mean square error is widely used in climatology, forecasting, and regression analysis to test experimental results.
actually = [0, 1, 2, 0, 3]predicted is [0.1, 1.3, 2.1, 0.5, 3.1]mse means sklearn. Metric. Mean_squared_error (real, predicted)rmse = math. square (ms)print (rmse)
Watch the video A quick tour of RMSE and its formula calculations:
- f = forecasts (expected values or unknown results),
- o = observed values (known results).
The distance between the squares of the differences is its mean (similar to xÌ “). Identical recipe ingredients can be written like this, but with slight differences (Barnston, 1992):
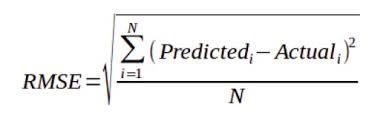
Where:
- Î £ equal
- (z f i – Z o i ) 2 = option , squared
- N = sample size.

You can use whichever formula works best for you, since they both do the same thing when compared. If you really don’t like formulas, you can buy RMSE:
- Squaring residuals.
- daily search for leftovers.
- Squares the root of the result.
When standardized observations and forecasts are used as input to the RMSE, there is a direct relationship with the correlation coefficient. For example, if the correlation coefficient is individual, the RMSE is 0 because almost all points lie on this regression line (and therefore there are simply no real errors).
Links
Barnston, A. (1992). “Correspondence between mean square error and Heidke’s test measures; Refinement of Heidke’s estimate. Notes – and therefore correspondence, Climate Analysis Center. Available here.
Kenny, J.F. and Keeping, E.S. Root Mean Square. § 4.15 on Mathematical Statistics, pp. 1, 3rd edition, Princeton, Van, NJ: Nostrand, pp. 59-60, 1962.
What do you mean by root mean square error?
Root mean square error (RMSE) would be the standard way to measure any error in a model to predict quantitative datasets. Formally, this is defined as follows: Let’s try to figure out why this error-related measurement makes sense from a numerical point of view.
Do you need help with homework or exam questions? Chegg Study gives you step by step answersLet us answer our questions from an expert in the field. Your first 30 minutes with Chegg’s teacher is
What is the root mean square deviation ( RMSE )?
Root mean square large difference (RMSD) or root mean square error (RMSE) is a widely used metric that measures the differences between values (sampled or multiple values) and those associated with observed values. RMSD is the square root of the first sampling time of the difference between the predicted values …
comments? is free! Need to write a fix? Please leave a comment on our Facebook page.
However, this can be computationally intensive, depending on the size of your dataset. Shortcut to find the root bar:
Where SD y is the norm, currently deviating from Y.
How do you calculate the root mean square error?
To compute the RMSE, compute the remainder (difference between prediction mean and truth) for each point in the file, compute a constant rate for each data point, compute all residual means, and then extract my square root from that mean.
What is RMS error value?
The root mean square error describes the differences between the values assumed by the model or your estimate and the actual observed values.
Why RMSE is used?
Since errors are squared before averaging, the RMSE assigns a relatively high weight to large errors. This RMSE method is especially useful when large errors are particularly undesirable.
Where is the Startup folder in XP?
Where is the Startup folder in Regedit?